Molecules | Free Full-Text | The Phosphorylated Form of the Histone H2AX (γH2AX) in the Brain from Embryonic Life to Old Age

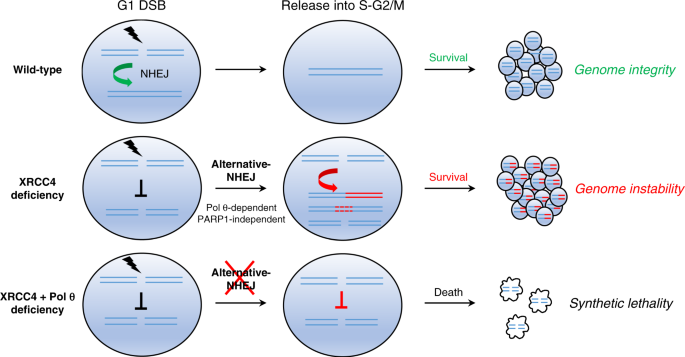
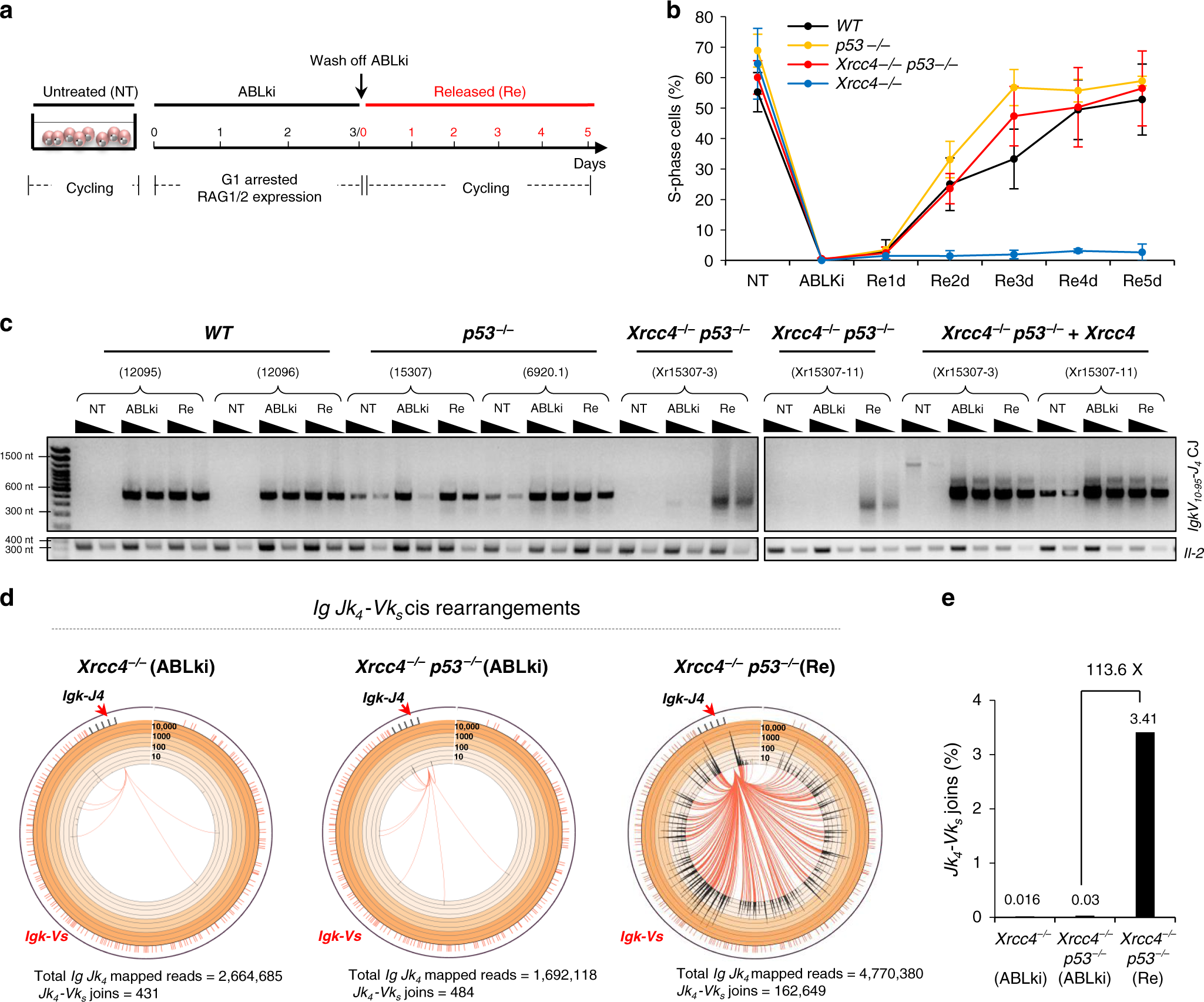
Impact of XRCC4 status on disappearance of G1-induced DSBs, (a) Left... | Download Scientific Diagram

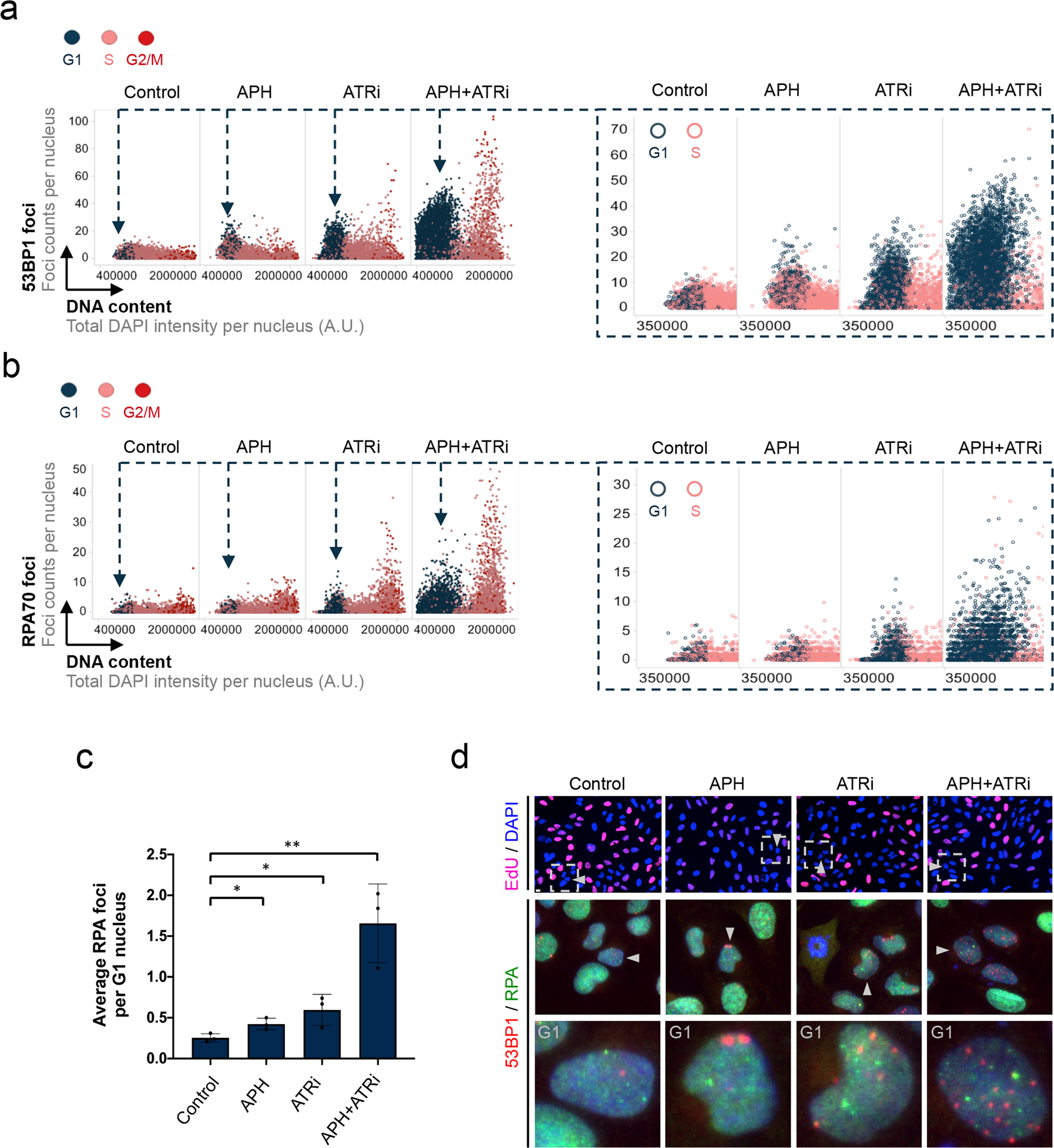
Quantifying cell cycle-dependent drug sensitivities in cancer using a high throughput synchronisation and screening approach - eBioMedicine
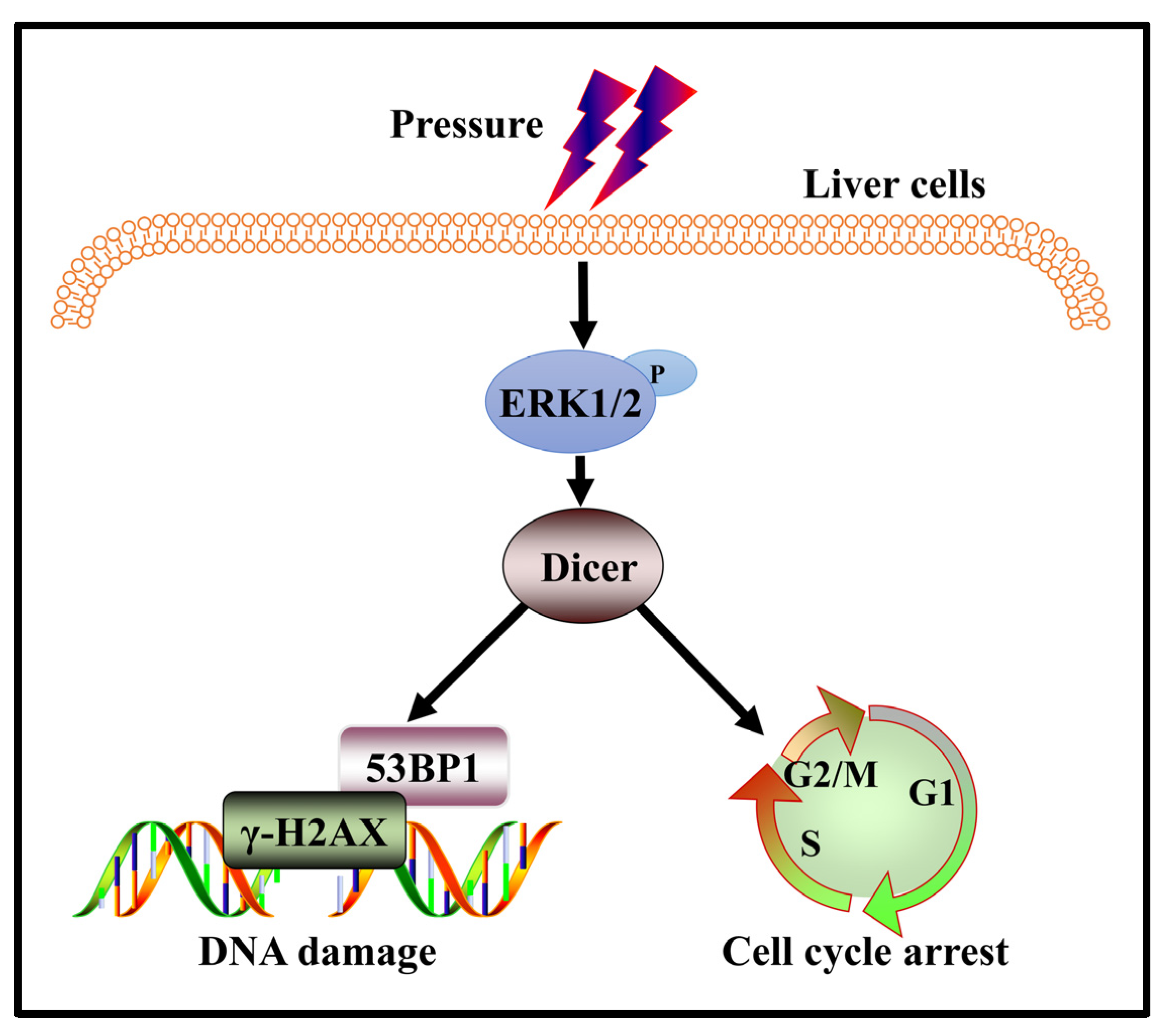
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Pressure Loading Induces DNA Damage in Human Hepatocyte Line L02 Cells via the ERK1/2–Dicer Signaling Pathway

Induction of DNA damage, apoptosis and cell cycle perturbation mediate cytotoxic activity of new 5-aminosalicylate–4-thiazolinone hybrid derivatives - ScienceDirect
Arrest of cell cycle progression at G1 and/or at G2/M in response to... | Download Scientific Diagram
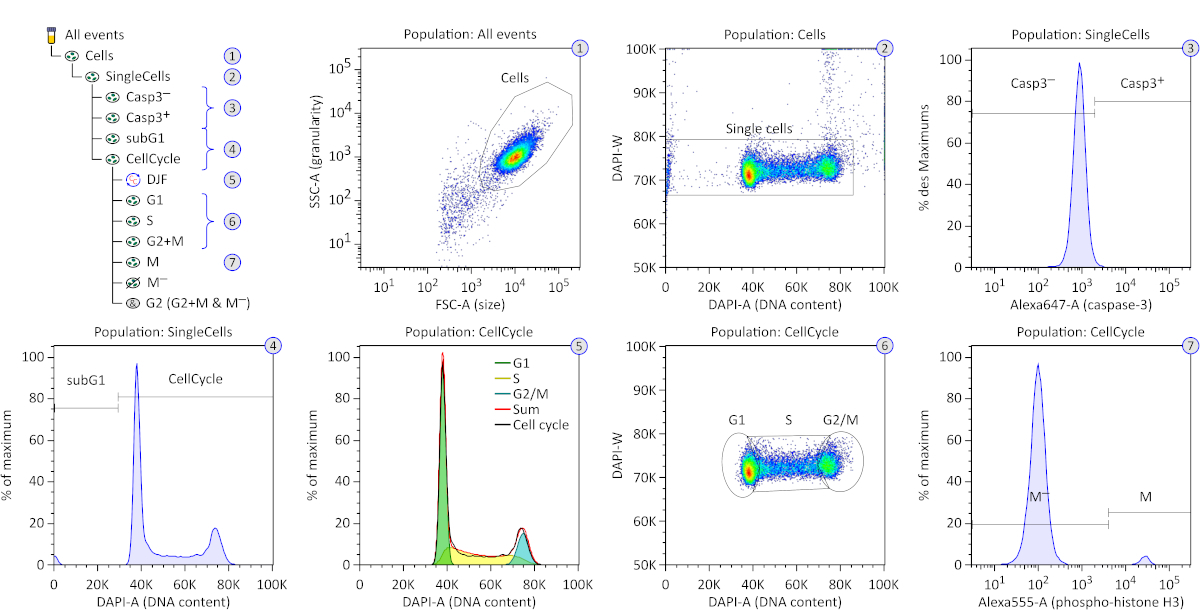
Cell Cycle-specific Measurement of γH2AX and Apoptosis After Genotoxic Stress by Flow Cytometry | Protocol

6G treatment induces DNA damage and G2/M cell cycle arrest in myeloid... | Download Scientific Diagram

Phosphorylation of H2AX associated with cell cycle progression and the... | Download Scientific Diagram
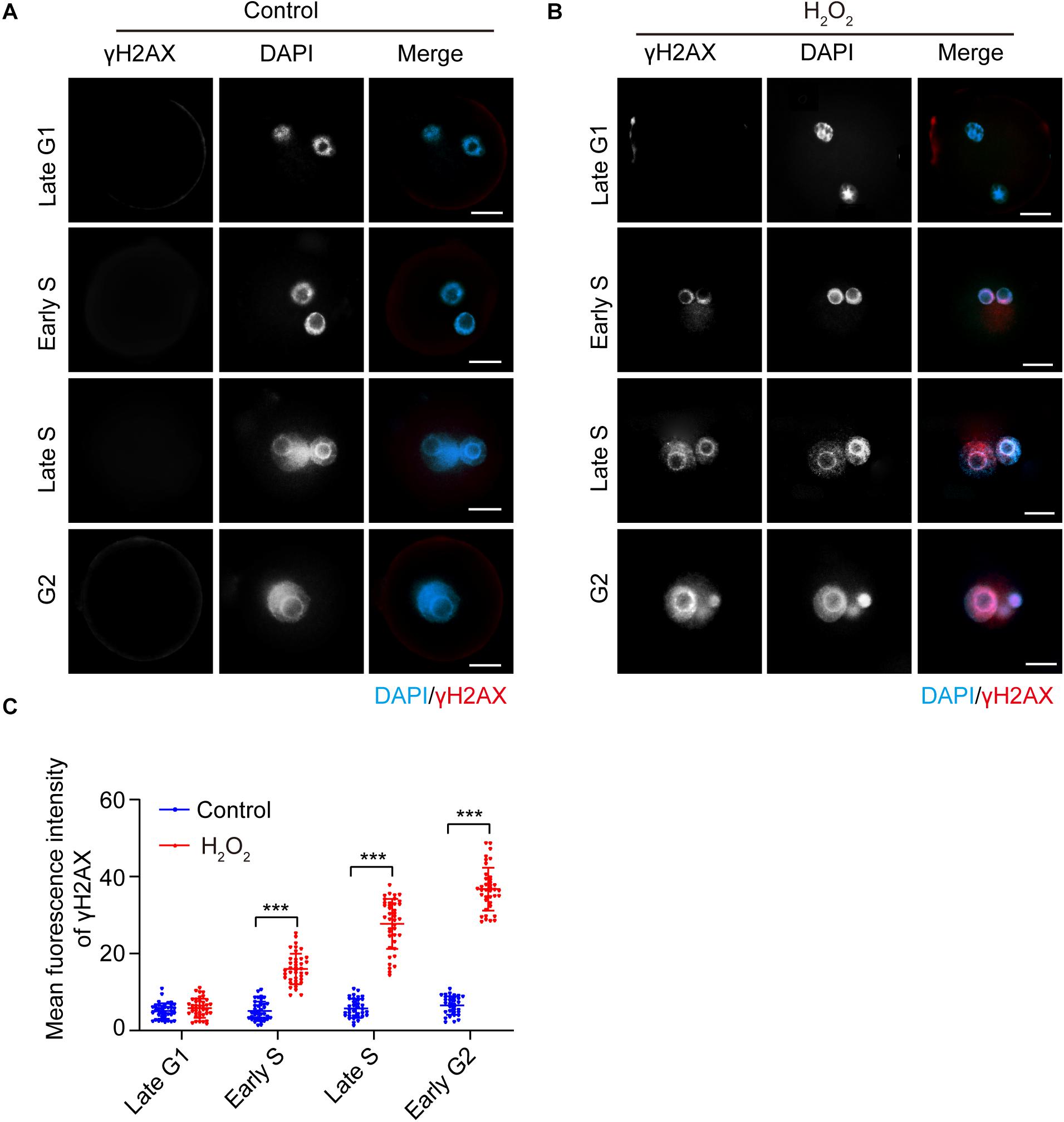
Frontiers | AMPK Activity Contributes to G2 Arrest and DNA Damage Decrease via p53/p21 Pathways in Oxidatively Damaged Mouse Zygotes
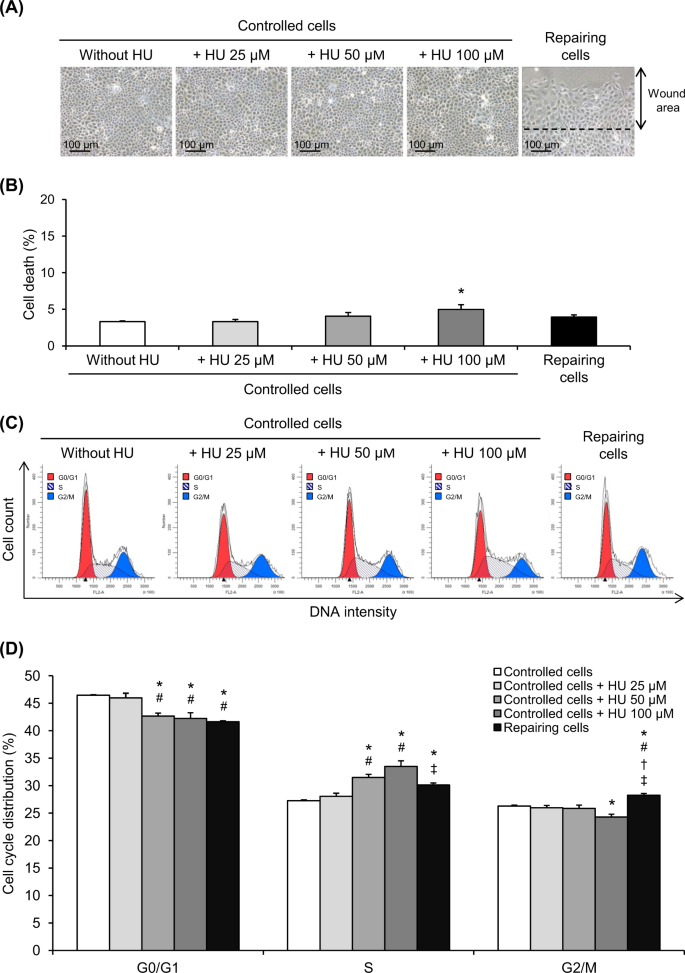
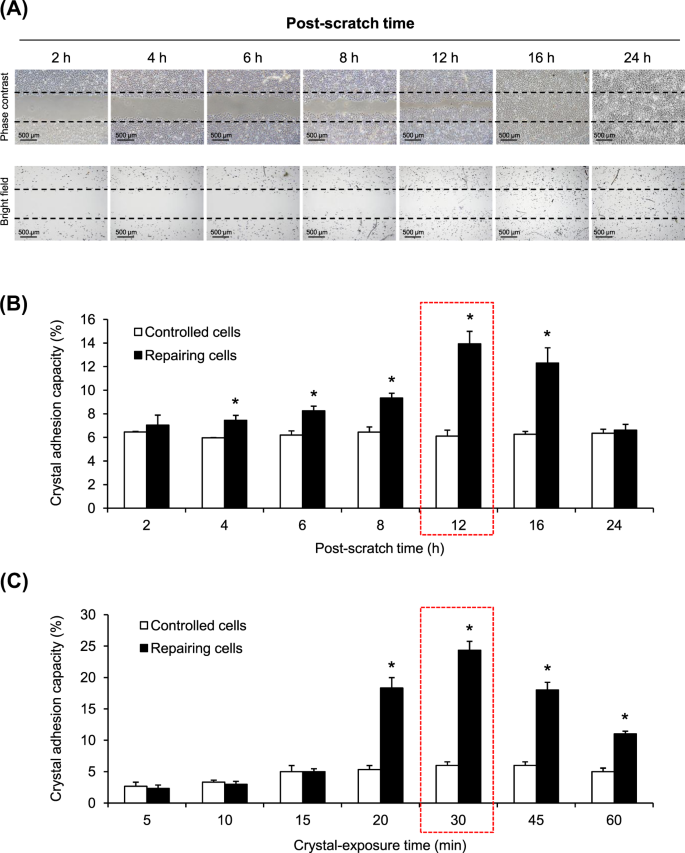
Cell cycle shift from G0/G1 to S and G2/M phases is responsible for increased adhesion of calcium oxalate crystals on repairing renal tubular cells at injured site | Cell Death Discovery

MI-res cells accumulate less cisplatin-induced DNA damage respect to... | Download Scientific Diagram
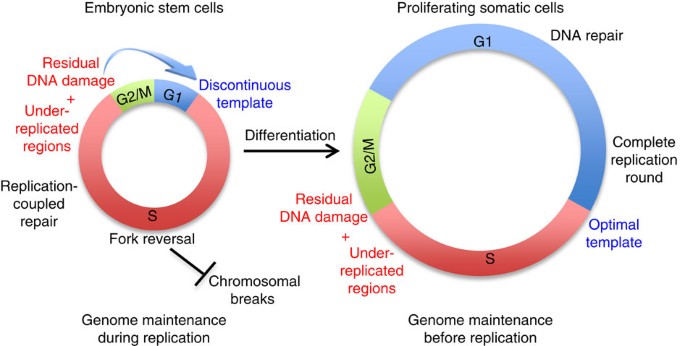
A short G1 phase imposes constitutive replication stress and fork remodelling in mouse embryonic stem cells | Nature Communications

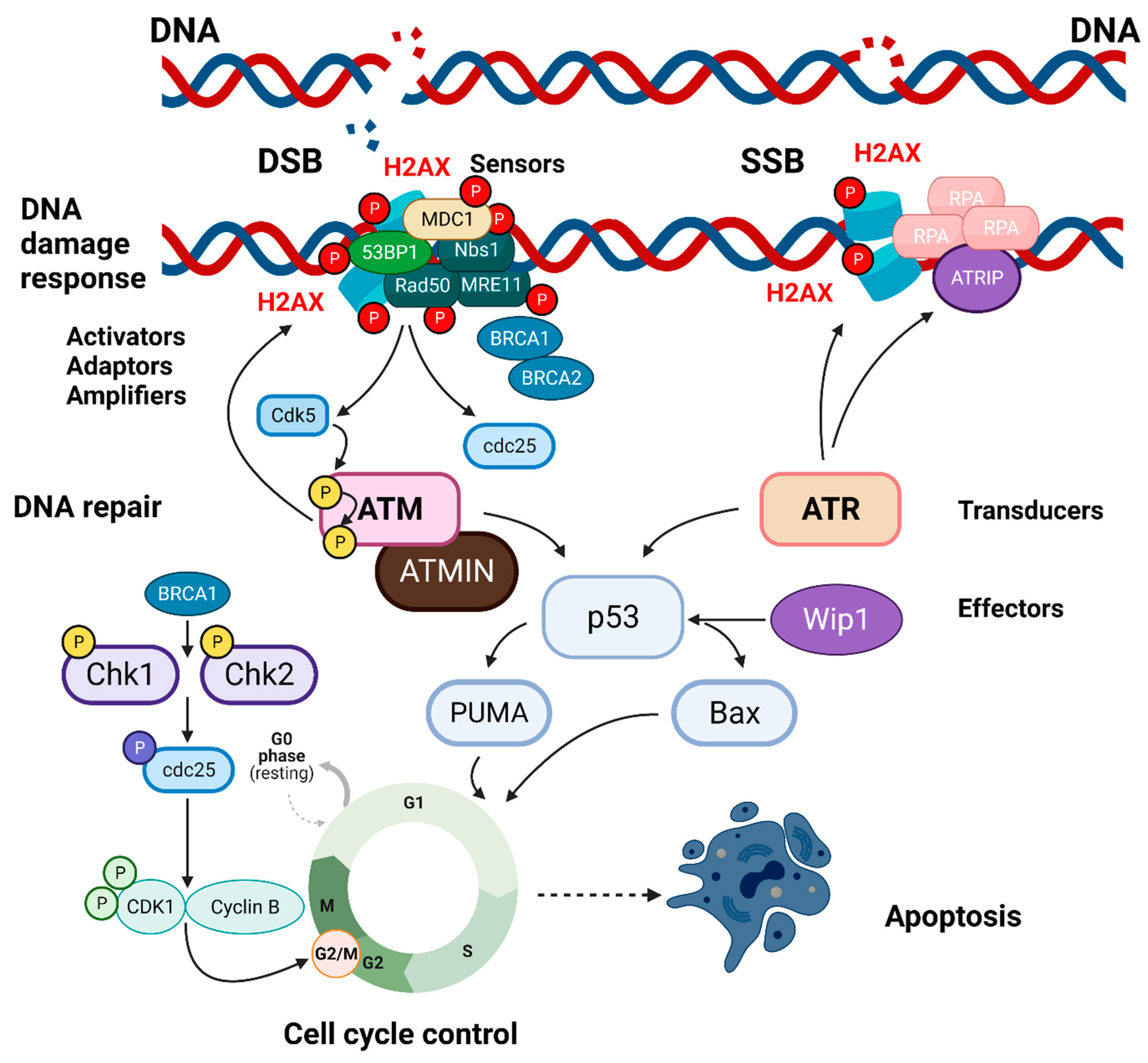
Conceptual representation of the signal transduction and of the central... | Download Scientific Diagram
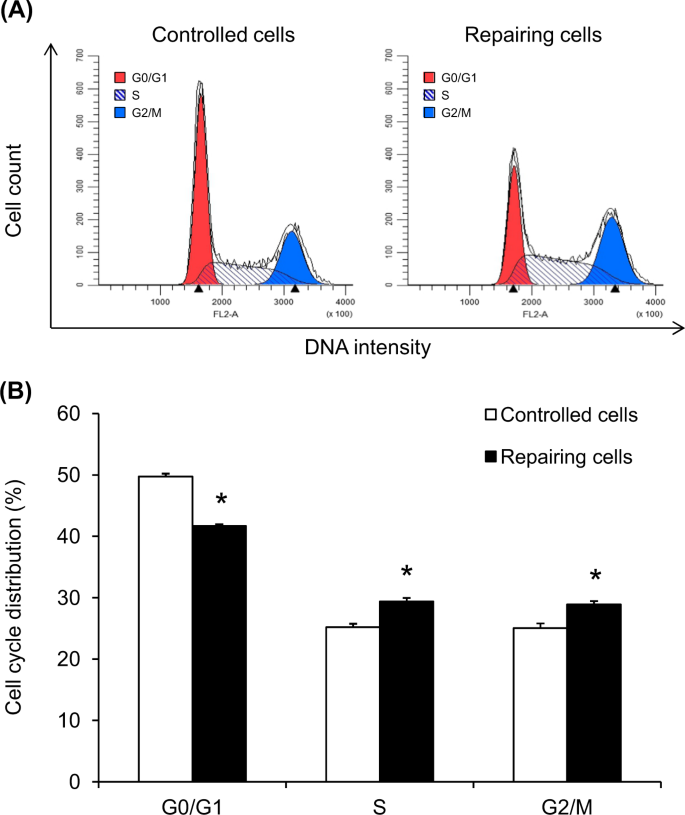
Cell cycle shift from G0/G1 to S and G2/M phases is responsible for increased adhesion of calcium oxalate crystals on repairing renal tubular cells at injured site | Cell Death Discovery

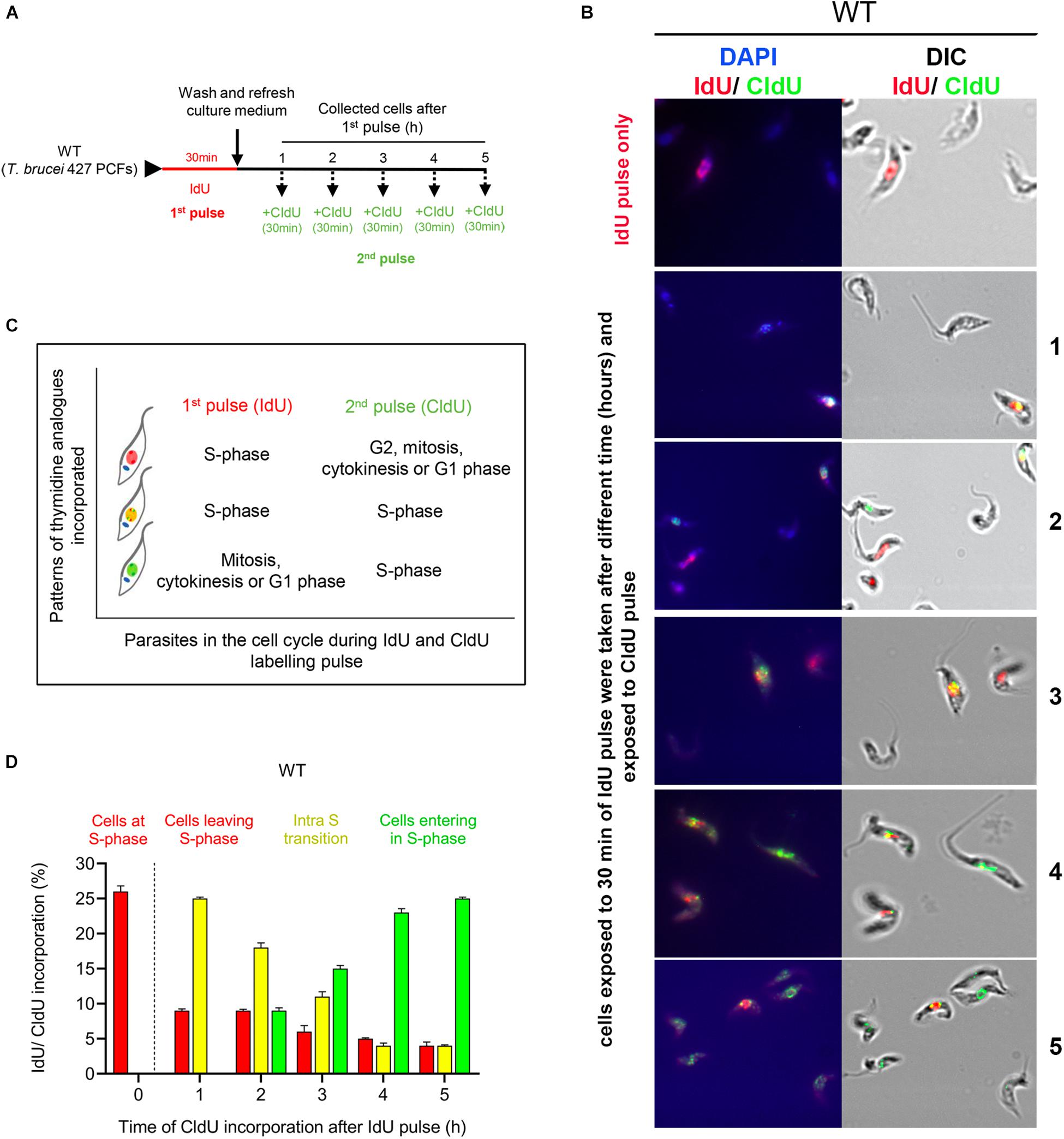
H2AX phosphorylation within the G1 phase after UV irradiation depends on nucleotide excision repair and not DNA double-strand breaks | PNAS